Maintaining your dog healthy weight is crucial to ensuring their overall well-being and extending their life. Just as in humans, being overweight or obese can significantly impact a dog’s health, leading to various chronic illnesses and reducing their quality of life. But with proper care, balanced nutrition, and regular exercise, you can keep your furry companion at an ideal weight. In this guide, we’ll cover actionable tips, what to avoid, and how to create a weight loss plan if your dog is overweight.
The Importance of a Healthy Weight

Dogs that maintain an ideal weight enjoy:
- Better Mobility: Excess weight puts strain on your dog’s joints, potentially leading to arthritis and reduced mobility, especially as they age. A healthy weight helps them stay active and mobile longer.
- Lower Risk of Illness: Obesity increases the risk of diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, high blood pressure, and respiratory problems in dogs.
- Improved Life Quality and Longevity: Studies show that dogs at an ideal weight live up to two years longer than those who are overweight. They also tend to have more energy, better digestion, and enhanced immune systems.
- Fewer Vet Visits: Obesity-related conditions, such as joint issues, heart problems, and diabetes, often require ongoing treatment and monitoring, leading to frequent vet visits and medical costs.
By prioritizing your dog’s weight management, you not only extend their lifespan but also ensure they live a healthier, more comfortable life.
How Can I Tell if My Dog is Overweight?
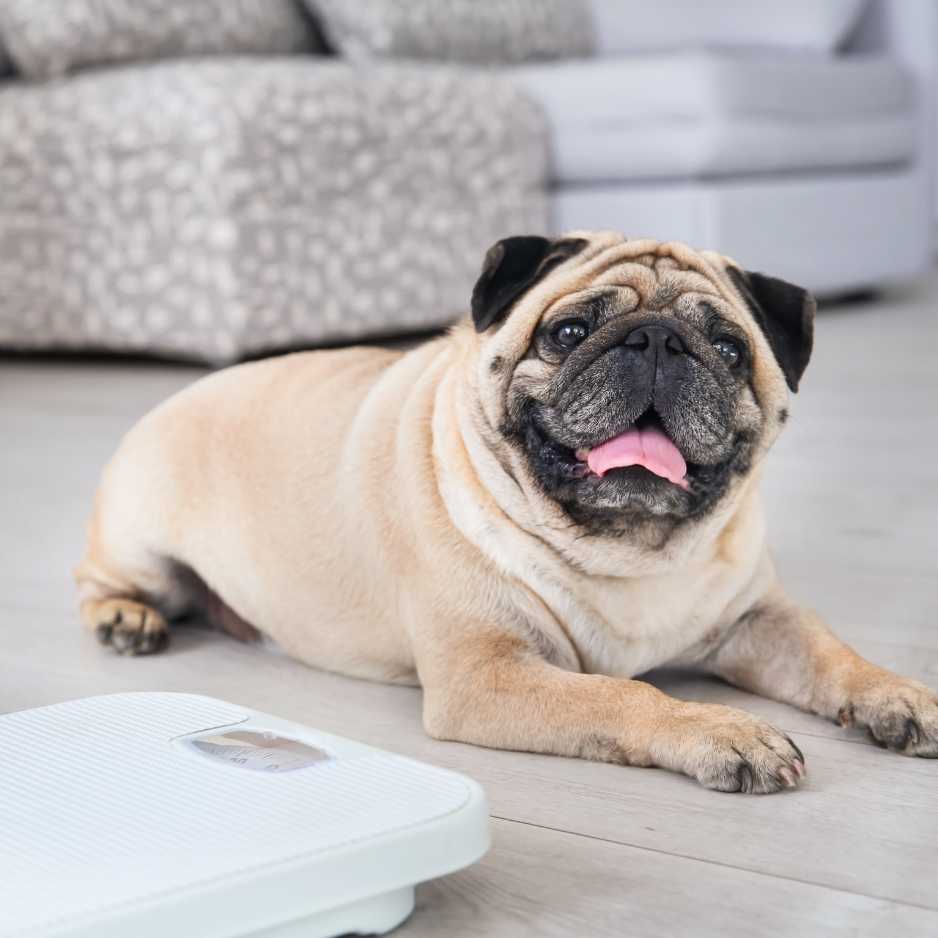

It’s important to determine if your dog is overweight so you can take the right steps to address it. Here are a few methods to assess your dog’s weight:
- Visual Inspection: When looking at your dog from above, they should have a defined waist that tapers behind the ribs. If they look more like a barrel or have no waistline, they may be overweight. When viewed from the side, there should be a noticeable upward tuck from the chest to the stomach.
- Feel Test: Gently run your hands along your dog’s sides. You should be able to feel their ribs without having to press too hard. If you can’t feel the ribs due to a thick layer of fat, your dog might be overweight. Conversely, if the ribs are too prominent, your dog may be underweight.
- Body Condition Score (BCS): Veterinarians often use a Body Condition Score (BCS) to evaluate a dog’s weight. The BCS scale ranges from 1 to 9, with 1 being extremely underweight, 5 being ideal, and 9 being obese. You can ask your vet to assess your dog’s BCS during a checkup to get a more accurate evaluation.
- Consult Your Vet: The best way to determine whether your dog is overweight is by consulting with your vet. They can assess your dog’s weight, body condition, and overall health and provide you with guidance on proper weight management.
By regularly checking your dog’s body condition, you can quickly identify any weight changes and take appropriate action to maintain their health.
What Are the Risks of Dog Being Overweight?

An overweight dog faces a variety of health risks that can significantly impact their quality of life and lifespan. Here are some of the most common risks associated with excess weight in dogs:
- Joint Problems and Arthritis: Extra weight puts added stress on your dog’s joints, which can lead to joint problems like arthritis. This is especially problematic for older dogs or breeds that are prone to hip and joint issues. Carrying excess weight accelerates wear and tear on the joints, causing pain and reduced mobility.
- Heart Disease and Hypertension: Overweight dogs are more likely to develop heart disease due to the added strain that extra weight places on their cardiovascular system. This can also lead to high blood pressure (hypertension), increasing the risk of heart attacks or strokes.
- Diabetes: Dogs who are overweight are at a much higher risk of developing diabetes. Excess fat in the body can cause insulin resistance, leading to high blood sugar levels. Managing diabetes in dogs requires lifelong medication, diet control, and frequent vet visits.
- Respiratory Issues: Excess fat can make it difficult for dogs to breathe properly, especially in breeds with shorter snouts like Bulldogs or Pugs. Obesity can lead to breathing problems, causing discomfort during physical activity and even at rest.
- Decreased Lifespan: Studies show that overweight or obese dogs have a shorter life expectancy compared to dogs that maintain a healthy weight. In fact, it’s estimated that overweight dogs live about 2 years less than their healthier counterparts.
- Reduced Quality of Life: Overweight dogs often have less energy and can experience chronic fatigue. Simple activities like walking, playing, or climbing stairs become more difficult and uncomfortable for them. As a result, overweight dogs may miss out on enjoying their day-to-day lives.
Maintaining a healthy weight is vital to preventing these risks and ensuring your dog lives a longer, healthier, and happier life. Regular weight monitoring, a proper diet, and exercise are essential to achieving and maintaining a healthy weight for your dog.
Assessing Your Dog’s Weight
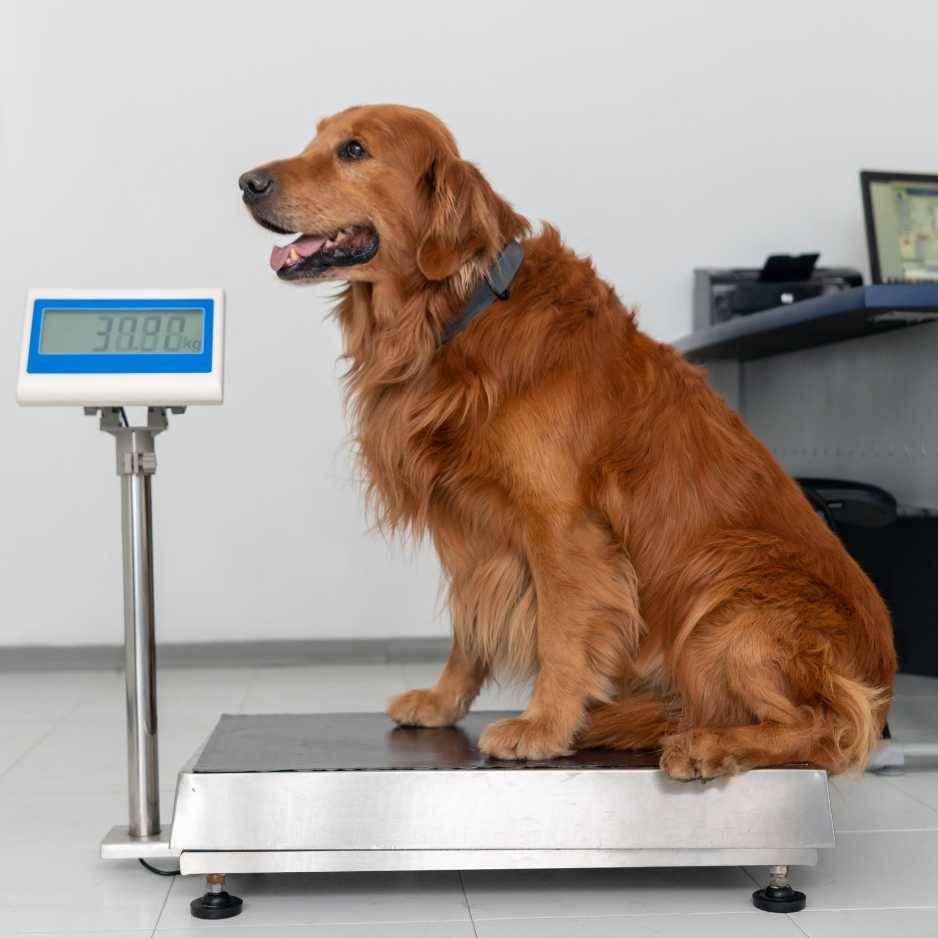
The first step toward controlling your dog’s weight is determining where they currently stand. There are a few methods for evaluating your dog’s weight and body condition:
- Body Condition Score (BCS): Veterinarians use the BCS scale to assess your dog’s body composition, typically rated from 1 to 9. A score of 1-3 indicates underweight, 4-5 is ideal, and 6-9 suggests overweight or obesity.
- Visual Check: When looking at your dog from above, you should see a noticeable waist behind the ribs, creating an hourglass shape. When viewed from the side, their abdomen should slightly tuck up toward the hind legs.
- Feel Test: Run your hands along your dog’s sides. You should be able to feel their ribs with only a thin layer of fat covering them. If you need to press hard to feel the ribs, your dog is likely overweight.
Steps to Maintain a Healthy Weight

One of the main reasons dogs become overweight is improper feeding habits. Ensuring your dog gets a balanced, nutrient-rich diet in appropriate portions is key to maintaining their ideal weight.
- Choose the Right Food: Opt for high-quality dog food that lists real meat as the first ingredient and has a balanced mix of proteins, fats, and carbohydrates. Avoid foods with fillers such as corn, wheat, or soy, as they offer little nutritional value and can contribute to weight gain.
- Control Portion Sizes: Overfeeding is one of the biggest culprits of weight gain. Always measure your dog’s food according to the guidelines provided on the packaging or recommended by your vet. Adjust portions based on your dog’s activity level, age, and breed.
- Scheduled Feeding: Stick to a regular feeding schedule, typically two meals a day. Avoid free feeding, where food is left out all day for the dog to eat whenever they want.
- Limit Treats: While treats are important for training and rewards, they should be limited to no more than 10% of your dog’s daily caloric intake. Opt for low-calorie treats or use healthy alternatives like carrots, green beans, or cucumbers.
Exercise is just as vital for dogs as it is for humans in managing weight.
- Daily Walks: Take your dog on regular walks, adjusting the duration and intensity based on their breed and age. A brisk 30-minute walk each day is generally a good starting point.
- Playtime: Engage your dog in interactive games like fetch, tug-of-war, or chase. Playtime helps burn calories and provides mental stimulation.
- Low-Impact Exercises: For older dogs or those with joint problems, activities like swimming are excellent for burning calories without putting stress on the joints.
- Puzzles and Toys: For mental engagement and light exercise, puzzle feeders and interactive toys can be used to keep your dog active indoors.
What to Avoid

Many dog owners unknowingly overfeed their pets by either giving them too large portions or offering extra treats throughout the day. Free feeding (leaving food out all day) can lead to uncontrolled eating, making it hard to manage your dog’s daily caloric intake.
It’s easy to forget that treats count toward your dog’s total caloric intake. Avoid giving too many high-calorie treats and instead choose low-calorie options or reduce the number of treats given throughout the day.
Human food, particularly processed or fatty foods, can add unnecessary calories to your dog’s diet and lead to weight gain. Additionally, some human foods like chocolate, onions, and grapes are toxic to dogs.
Creating a Weight Loss Plan

If your dog is overweight, it’s important to follow a structured weight loss plan to bring them back to a healthy weight. Here’s how to create one:
Consult your vet before starting a weight loss plan to ensure it’s safe for your dog and tailored to their individual needs.
- Determine Ideal Weight: Your vet will calculate your dog’s target weight based on their breed, size, and overall health.
- Caloric Needs: Your vet will determine how many calories your dog should consume daily to achieve a steady weight loss, typically reducing their intake by 10-20%.
Switching to a low-calorie, high-protein dog food designed for weight management can help your dog shed pounds without feeling hungry.
- High Fiber Content: Foods rich in fiber help your dog feel fuller for longer.
- Portion Control: Measure food carefully to ensure you’re feeding the correct amount based on your dog’s caloric needs.
Overweight dogs may not be able to handle intense exercise right away. Start slow with low-impact activities like short walks or swimming, and gradually increase the intensity and duration of their exercise as they lose weight.
Track your dog’s weight loss journey by weighing them regularly and keeping a journal of their food intake and exercise. Aim for slow, steady weight loss (around 1-2% of their body weight per week).
Monitor and Adjust for Long-Term Success

Even after your dog reaches their ideal weight, maintaining it requires ongoing attention.
- Reassess Caloric Intake: As your dog’s weight and activity level change, so do their caloric needs. Adjust their food portions as needed to avoid rebound weight gain.
- Regular Exercise: Continue to provide regular exercise to keep your dog fit and healthy long-term.
- Vet Checkups: Keep up with regular vet visits to monitor your dog’s weight and address any changes in health or behavior.
Conclusion
Helping your dog maintain a healthy weight is one of the best things you can do to ensure their long-term health and happiness. By following proper nutrition guidelines, exercising regularly, and monitoring their weight, you can keep your dog fit and avoid the health risks associated with obesity. If your dog is overweight, creating a structured weight loss plan in consultation with your vet will help them achieve a healthier weight safely and effectively. Remember, maintaining a healthy weight requires consistency, patience, and ongoing effort—but the reward is a longer, happier life for your beloved pet.
FAQs: How to Control Your Dog’s Weight for a Longer, Healthier Life
What if my dog begs for more food and seems upset when I don’t give it?
It’s common for dogs to beg for food, especially if they’re used to getting more than they need. Here are some strategies to manage this behavior:
Exercise and mental stimulation: Boredom often leads to begging. Increase your dog’s exercise and mental stimulation with activities like walks or puzzle toys.
Stick to the plan: Resist the urge to give in to begging. Remember, maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for your dog’s well-being.
Distract with toys or affection: Engage your dog with a toy or some attention instead of extra food.
Use low-calorie treats: If you need to give something extra, offer low-calorie treats like carrots or green beans to satisfy their craving without adding many calories.








